KPI – Key Performance Indicator
Key Performance Indicators, or KPIs, are quantifiable metrics used by organizations to evaluate their performance in achieving specific objectives. These objectives could range from financial targets to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Essentially, KPIs act as navigational tools, guiding businesses towards their desired outcomes by providing measurable indicators of progress.
Types of KPIs KPIs can be broadly categorized into four main types:
- Financial KPIs: These focus on the financial aspects of the business, such as revenue growth, profitability, and return on investment (ROI).
- Operational KPIs: These assess the efficiency and effectiveness of operational processes within the organization, including production output, delivery times, and resource utilization.
- Customer KPIs: Customer-centric KPIs measure satisfaction levels, retention rates, and acquisition costs, reflecting the business’s ability to meet customer needs and expectations.
- Employee KPIs: These gauge employee performance, engagement, and productivity, contributing to overall organizational success.
Calculating KPIs Let’s consider an example of a retail company aiming to measure its sales growth over a specific period. The formula for calculating sales growth as a percentage is:

For instance, if the company’s sales were £500,000 in the current period and £450,000 in the previous period, the sales growth would be:
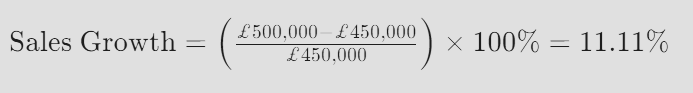
This calculation indicates an 11.11% increase in sales over the period, providing valuable insight into the company’s performance.
Conclusion In today’s competitive business environment, success hinges on more than just intuition; it requires data-driven decision-making. Key Performance Indicators serve as vital instruments in this pursuit, offering businesses a means to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately, drive success.











